Cartilage is a rigid but elastic tissue that cushions the ends of bones where they meet within a joint. It is found in many places, such as joints, nose, ears, and at the end of ribs. The primary function of the cartilage is to act as protection and provide stability for those joints. Additionally, there are some other functions of cartilage. For instance, the articular cartilage helps reduce joint friction; it also helps bind the bones together and maintain the volume of synovial fluid.
While bones comprise cells, liquids, and minerals, which provide structure and strength, cartilage comprises cells and extracellular matrix molecules. In addition to providing mechanical support for weight-bearing joints such as knees, elbows, and wrists, cartilage supports the connective tissue system by maintaining tissue shape.
What is the Difference?
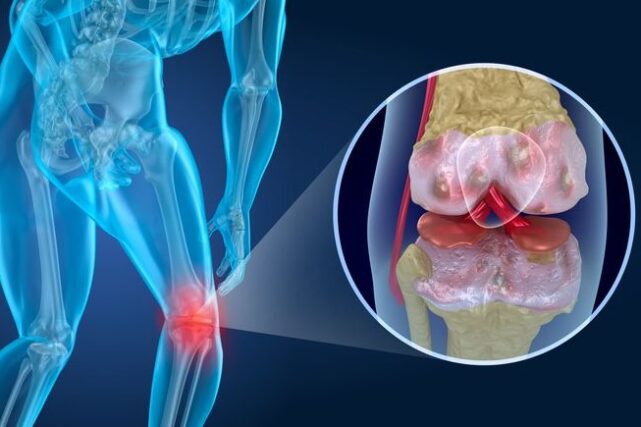
Cartilage and bones are very different. This statement is because the cells in bone divide and repair the damage done to their DNA during the aging process, a process known as osteogenesis. However, this does not occur in cartilage, a non-regenerative tissue. The cells in cartilage do not divide; hence, there is no replacing dead cells with living ones. As a result, cartilage injuries remain permanent even without surgical repair. The joints are protected by ligaments and tendons that support them when they move. When there is an injury above them, it will cause pain at the joint sites because those tissues cannot heal themselves.
While bone injuries can be repaired and healed by the body, cartilage injuries can not be repaired. There are several reasons why bones heal faster compared to cartilage. The primary cause is that bones have a rich blood supply, which means the cells will multiply and divide rapidly. However, since cartilage lacks a good blood supply, the cells remain inactive and unable to regenerate or split after an injury. Instead of dividing and renewing, injured cartilage cells die silently and slowly as time passes by. Once dead, those with no bone beneath will begin forming a soft mass or thickening within three to five months of the initial injury. The body will then take on a fibrous texture with scaly lesions and scarring.
Despite this, there are instances where injured cartilage does heal. In babies and young children, the ear cartilage can regenerate itself once a hole has been created. The same goes for the knee cartilage when you bend it more than it was supposed to be bent and overstretch the ligaments. In this case, the articular ends heal within a few days after spraining. However, in adults, once an injury happens to the joint, it is impossible to recover it again because of how mature our bodies have become.
There are, however, several treatments for damaged cartilage. Some of them are conservative such as weight loss, physical therapy programs, and medication to relieve the pain and inflammation in the affected area. Other conventional treatments include cortisone shots and cross-linking. It involves injecting the cartilage with an added enzyme called chondroitinase that breaks down cartilage components, thus boosting the healing process. On the other hand, if it is impossible to repair the injured cartilage cells at all, then one has to undergo surgical treatment such as arthroscopy, where a microscope is inserted into an opening within a joint, which allows a surgeon to make all improvements required.
Common Treatments For The Most Common Joint Injuries

1. Injections of Platelet-Rich Plasma
Platelet-rich plasma contains platelets, which are cells that help in blood clotting and healing. They are extracted from blood donors, or they can be purchased from laboratories to use as injections. These injection treatments are good in treating cartilage injuries because they will help enhance the regeneration process of the joint, thus improving its stability and strength.
2. Joint Injections
There are various injections available to treat patients with fractures and joint injuries. These injectables that can restore certain joints to their normal condition include hyaluronic acid, synovial fluid injections, and intervertebral injections. These are all very effective in healing cartilage injuries because they help boost the structural integrity of the joint by increasing the fluid volume within it.
3. Surgery
While some cases are managed surgically, there will undoubtedly be some that would require surgeries to remove damaged cartilage and fix other injuries present within the same joint. The best option for this is arthroscopy, which involves making an opening into the damaged joint for a surgeon to gain access to it. While a tiny camera is used to see what is happening inside, another surgical instrument operates on the damaged area. Once this part of the surgery has been done successfully, the orthopedic surgeon can make all necessary repairs to the injured cartilage.
4. Osteotomy
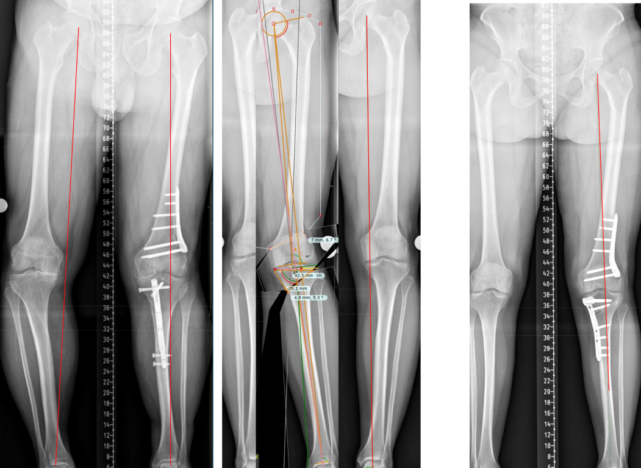
Osteotomy means cutting and moving a bone for medical reasons. It is one of the best options for treating cartilage injuries in joints because it will help immobilize them by taking off weight-bearing loads that can cause further damage to the joint.
5. Acupuncture
Acupuncture, also known as Chinese medicine treatment, is inserting needles into specific points in the body to stimulate blood flow and improve health. It has been used to treat various diseases, including joint and cartilage injuries. It is done in multiple ways, such as inserting needles into specific points of the body or using acupressure points on particular areas. The acupuncture treatments will make it easier for damaged cartilage to heal by causing blood circulation that helps carry oxygen and nutrients to damaged tissues to help them regrow or repair themselves.
6. Infrared Sauna
The infrared sauna is a well-known treatment for cartilage injuries because it will help promote blood circulation by helping warm up the body tissues, thus increasing blood flow through the damaged areas of bone and cartilage. It will also increase the elimination of toxins from within the body and helps to detoxify the system, thus improving its overall health.
7. Ultrasound Training
Ultrasound training is a non-invasive type of treatment involving using ultrasound waves to vibrate specific parts of those with joint problems to stimulate healing processes within damaged tissues. It is a lesser-known treatment for sports injuries, which is why a few specialists in the country only look into it.
8. Mesotherapy
It is an injection treatment that involves injecting various compounds directly into the destroyed joint cartilage. These compounds include hyaluronic acid and other growth factors that can make the regrowing process easier on certain damaged parts of joints by stimulating regeneration processes. Hyaluronic acid injections also help build larger, thicker cartilage surfaces. In contrast, others block off specific molecules within the cartilage cells to help outside forces be absorbed or prevented from entering.
Although cartilage injuries are prevalent, fixing them is not always easy. However, plenty of treatment options are available to help you with this issue. You must consider each option carefully and decide which option will be best for you. Then you will have to see a professional physician and follow whatever course of treatments your doctor recommends for your cartilage injury to fully heal so that you do not experience any more pain in the joint and be able to engage in your usual daily tasks without feeling any discomfort. Once the cartilage is damaged, it can often be excruciating and may need to be replaced.
There are various ways to fix multiple forms of cartilage injuries. Depending on the type of injury one has sustained, there will be varying techniques for improving it. You must first assess what damage you have sustained, check for any joint abnormalities such as synovial fluid or bone loss, and check for any severed ligaments that need to be reconstructed. Each of these will also vary and may require different types of treatment.
Once all the critical injuries are assessed, one can begin their treatment plan by looking into injections or surgeries to reconstruct damaged cartilage within their knee or hip joints.